Sustainability Purpose and Development Mission
Fu Jen Catholic University Hospital adopts a sustainable healthcare model that promotes harmony with nature and addresses climate challenges as its primary environmental sustainability goal. The hospital is committed to upholding the principles of honest and transparent governance (Truth), respecting the values of life and care for all beings (Goodness), creating healthy and comfortable healing spaces (Beauty), and fulfilling its spiritual responsibility toward the Earth and future generations (Holiness). Environmental responsibility is regarded as an integral part of the hospital's medical mission. Through institutionalized ecological management and the application of innovative technologies, the hospital actively promotes energy conservation and carbon reduction, water resource conservation, waste reduction, and green procurement, progressively building a resilient and forward-looking sustainable healthcare environment.
In terms of medical waste management, the hospital continues to advance transparency in information disclosure and source-based waste separation. Fostering diverse partnerships strengthens the efficiency of resource recycling and circular utilization. Moreover, the hospital proactively addresses climate change by integrating sustainability perspectives into healthcare facility planning and operational decision-making. These efforts not only safeguard patient health and well-being but also embody the shared mission of protecting the Earth's ecosystems and the future of the next generation, thereby fulfilling its commitment to environmental sustainability through concrete actions.
TCFD and Resilience Adaptation Measures
In response to the intensifying impacts of climate change and the rising frequency of extreme weather events, Fu Jen Catholic University Hospital follows the four core pillars of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) framework to establish a climate governance mechanism. Through this framework, the hospital systematically assesses both operational and financial risks and opportunities, sets medium- and long-term carbon reduction targets, and progressively advances toward the goal of becoming a net-zero hospital by 2050.

Climate Risk and Opportunity Identification Process
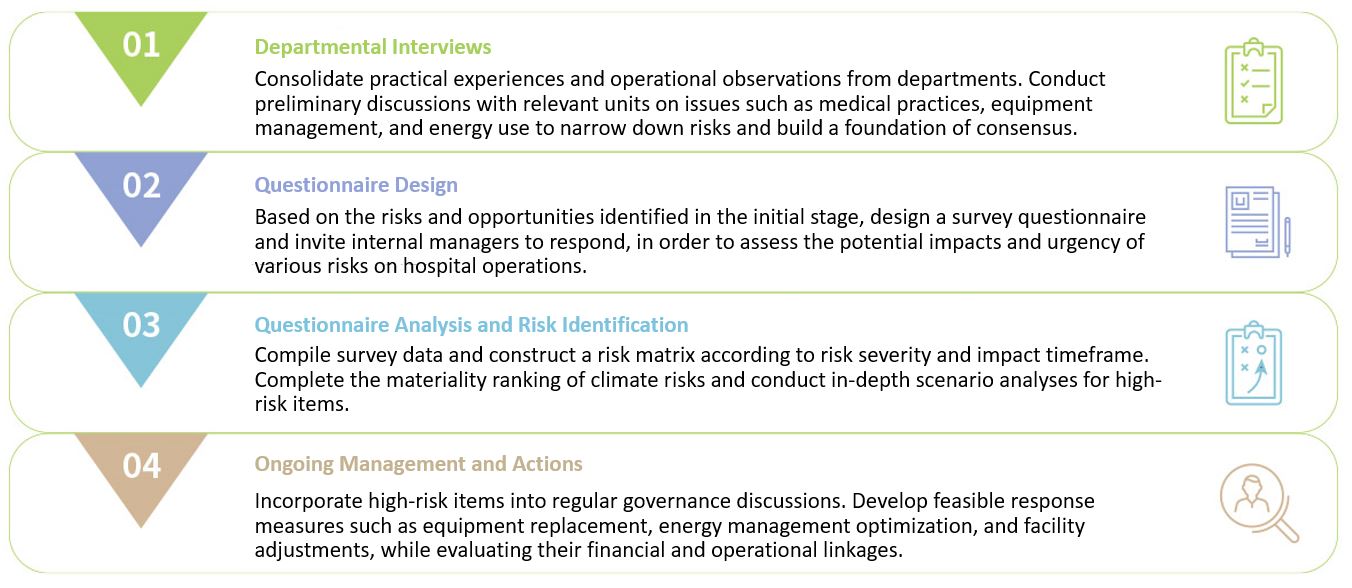
Climate Risk and Opportunity Classification and Financial Assessment
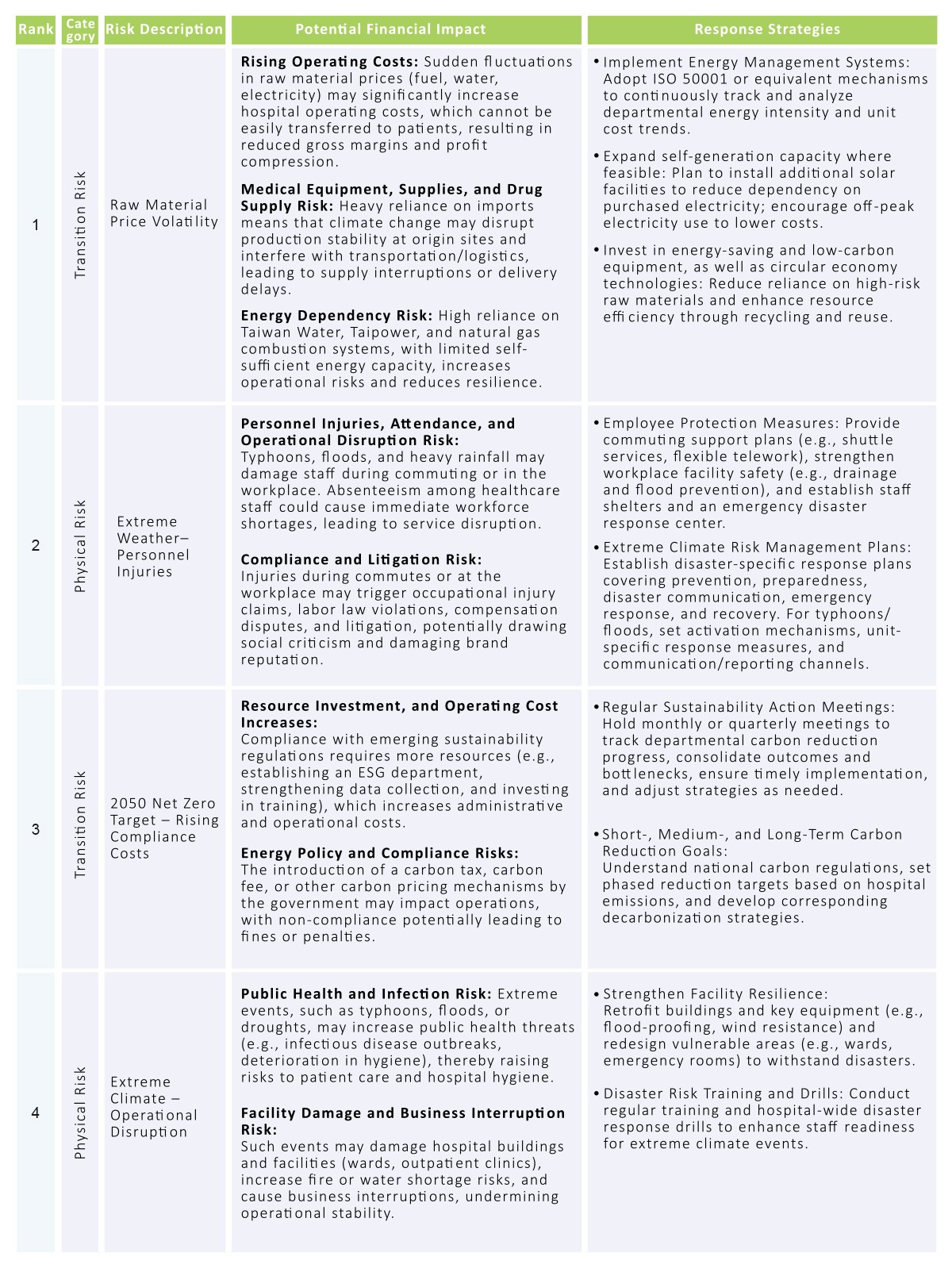
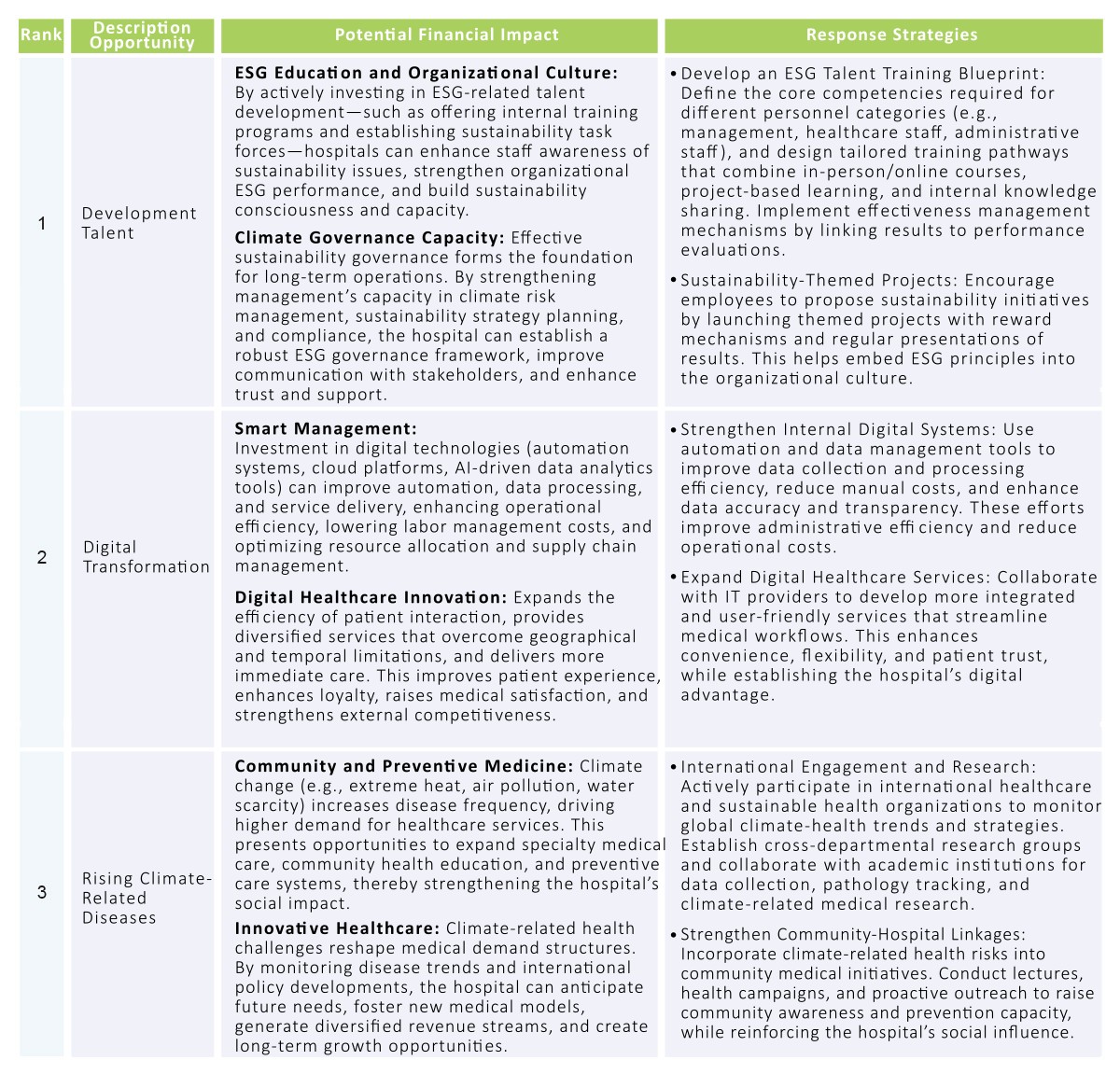
Energy Optimization and Carbon Reduction
To monitor overall energy use and continuously optimize management efficiency, FJUH compiles annual data on total hospital electricity consumption, departmental electricity share, and primary energy-intensive sources. High-consumption equipment such as refrigeration and air conditioning systems, operating rooms, and large medical instruments are key focus areas. Their performance is continuously tracked through the hospital's energy monitoring system to support energy planning and efficiency improvement measures.
Fu Jen Catholic University Hospital, in response to international climate frameworks such as the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the Paris Agreement, actively fulfills its environmental protection responsibilities. The hospital has adopted standards including ISO 14064-1:2018, the GHG Protocol Corporate Standard, and the Guidelines for Greenhouse Gas Inventories to conduct comprehensive carbon inventories.
The scope of the inventory covers Category 1, Category 2, and Category 4 emissions, ensuring full monitoring of greenhouse gas impacts throughout hospital operations. Emission factors are derived from official data published by Taiwan's Ministry of Environment, with calculations based on activity data such as natural gas consumption and purchased electricity.
Fu Jen Catholic University Hospital continues to implement energy-saving and carbon-reduction measures, enhancing energy efficiency and utilization through building design, equipment replacement, system management, and cross-departmental collaboration. By introducing green building concepts and implementing high-efficiency equipment replacement programs, as well as participating in government energy-saving benchmarking competitions, establishing the ISO 50001 Energy Management System, and receiving external consultancy guidance, the hospital has developed a systematic energy management process across its campus.
To demonstrate the hospital's achievements in energy conservation and carbon reduction, the General Affairs Office launched the "Love Sustainability – Continuous Energy Saving and Carbon Reduction" project, which was awarded the 2024 SNQ National Quality Certification, valid through the end of 2025.
This project encompasses the replacement of lighting systems, energy-saving management of HVAC systems, equipment upgrades, and the implementation of administrative energy-saving policies. Through cross-departmental collaboration, the hospital has strengthened energy efficiency management and carbon reduction measures, earning national-level recognition for its sustainability efforts.

Smart Water Management and Circular Reuse Strategy
The hospital places great importance on sustainable water resource management. Based on routine inspections and meter monitoring records, regular assessments of water usage are conducted to track consumption patterns and identify trends in high-usage areas. In 2024, the hospital's total water consumption reached 216,640 cubic meters, primarily sourced from third-party water suppliers.
Water-Saving Measures and Efficiency Enhancement Practices
In response to the growing demand for medical water usage, Fu Jen Catholic University Hospital has actively introduced water-saving technologies and management measures to reduce resource consumption and enhance utilization efficiency. Future initiatives include the recovery of air-conditioning condensate water, reuse of wastewater discharged from RO (reverse osmosis) water purification systems together with condensate drainage and rainwater harvesting, as well as establishing recycling mechanisms for cooling towers, evaporators, and other high water-consuming equipment.
Waste Reduction, Recycling, and Resource Regeneration
In 2024, the hospital's total waste output amounted to 797,811 metric tons, of which approximately 37.89% was biomedical waste, 57.44% was general waste, and 4.67% was recycled. The hospital continues to promote waste reduction measures and source-based waste separation, while tracking waste generation indicators annually to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of reduction efforts.



